Cash and cash equivalents are both included in the definition of cash flows. The cash flow statement explains the difference between the beginning and ending cash and cash equivalent balances. We Continue to use the terms cash flows and cash flow statement, but keep in mind that Both terms refer to money and money equivalents. Remember that a currency equivalent must meet two requirements. criteria:
(1) be easily convertible to a known quantity of cash; andClassification of Cash Flows
Because cash transactions are merged, transactions between cash and cash equivalents, such as cash spent to acquire cash equivalents and cash received from selling cash equivalents, are not reported on the statement of cash flows. All other cash receipts and payments, on the other hand, are categorized and recorded on the statement as operating, investing, or financing operations. Individual cash receipts and payments for each of these three categories are tagged to indicate the transactions or events that generated them. A net cash inflow (source) happens when a category's receipts exceed its payments. When the payments in a category exceed the revenues, there is a net cash outflow (use).
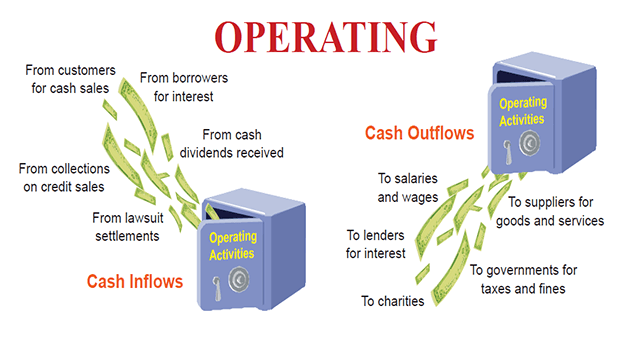
Operating Activities
The transactions and events that determine net income are referred to as operating activities. Examples include the manufacture and procurement of commodities, the selling of goods and services to clients, and administrative expenses. Not all revenue items, such as exceptional profits and losses, are operating activities (these exceptions are discussed later in the chapter). Exhibit 16.1 shows the most frequent cash inflows and outflows from operations. (While cash receipts and cash payments from purchasing and selling trading securities are frequently reported as operational activities, new rules demand that these receipts and payments be categorised depending on the nature and purpose of the securities.)
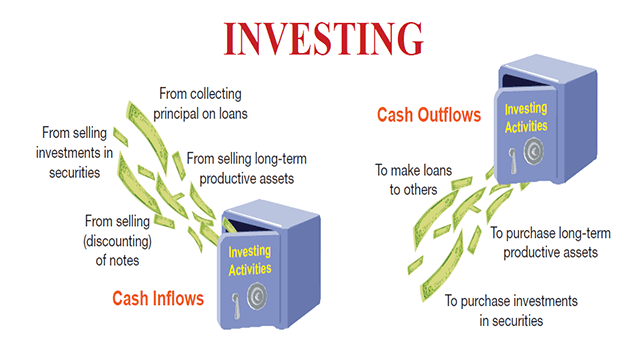
Investing Activities
Generally, investing activities include transactions and events that influence long-term assets, such as the acquisition and sale of long-term assets. They are also include1)) the acquisition and sale of short-term investments in other businesses' securities other than cash equivalents and trading securities, and (2) lending and collecting money for notes payable Exhibit 16.2 shows several instances of cash flows generated by investment operations. Special mention should be made of the proceeds from collecting the main amounts of notes. If the note is the result of client sales, the cash receipts are classified as operating activities, whether short-term or long-term. However, if the note is the outcome of a loan to another party rather than a sale, the cash proceeds from collecting the note principal are classified as an investing activity. The FASB mandates that interest on loans be recorded as an operational activity.
Financing Activities
Financing activities encompass all transactions and events that have an impact on long-term obligations and equity. Examples include (1) collecting cash from issuing debt and repaying the amounts borrowed, and (2) receiving or distributing cash to owners. These operations entail dealings with the owners and creditors of a corporation. They frequently include borrowing and repaying principal amounts for both short- and long-term debt. Payments of interest expense must be classed as operational activities under GAAP. Cash payments made to settle credit purchases of items, whether on account or by note, are also considered operational operations. Exhibit 16.3 illustrates cash flows resulting from financing operations.Cash Monitoring To improve or diminish current period cash flows, cash flows might be postponed or accelerated at the conclusion of a period. Cash flows can also be misclassified. Expense payments are understood as cash withdrawals reported under operations. Cash outflows recorded under investment activities, on the other hand, are seen as a good indicator of future growth potential. As a result, managers have an incentive to misclassify cash flows. For these reasons, cash flow reporting deserves our attention.